
There are a few misconceptions about the concept of digital libraries. Perhaps the most common is that they exist to replace physical libraries. But when we break down the question, “what is a digital library?” that theory is quickly debunked.
By its simplest definition, a digital library is an online collection of files that can be accessed on the internet. As we further define digital libraries and their uses, we will explore the benefits they play in education and why all schools should utilize digital libraries.
What Is the Purpose Of a Digital Library?
For those who are less comfortable with the idea of digital libraries, it’s easy to believe that they were created to replace traditional library services. But as Lee A. Paradise points out, “the existence of one doesn’t have to mean the demise of the other.”
In reality, digital libraries were created to work in tandem with physical libraries. They exist to preserve the resources found in traditional libraries and increase the circulation of information using an online database with digitized titles.
You can find anything that you would in a standard brick-and-mortar library—and more— inside of a digital library: books, magazines, newspapers, videos, audio recordings, and photographs.
Yet, digital libraries make the acquisition of these resources easier because they can be accessed anywhere with an internet connection.
Advantages of a Digital Library
There are so many advantages of digital libraries that can’t be overlooked, especially when it comes to education. Below are six of the indisputable advantages that digital libraries have over physical libraries.
1. Remote Access Anywhere, Anytime
This is one of the greatest benefits of digital libraries. Students can read titles anywhere with an internet connection. They aren’t restricted by library hours or transportation limitations. Plus, they don’t have to lug multiple heavy textbooks around.
These are desirable features for students with busy schedules like those participating in sports or extracurricular activities. If they don’t have time to make it to the library during regular hours, digital libraries give them the freedom to log on later when their schedule allows.
If they don’t have access to the internet, most digital library databases like ProQuest E-Book Central permit downloadable PDF versions to be saved on the computer or printed, allowing for learning on the go — on the bus, in the car, on vacation, wherever they please.
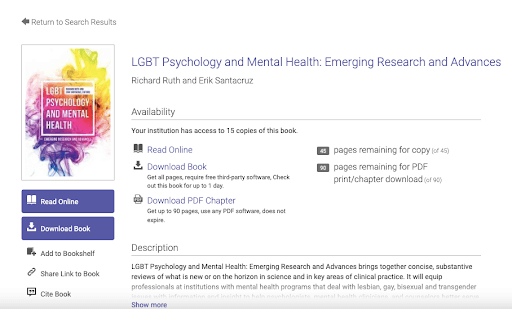
2. Accessibility Features
Most e-books or articles found within digital libraries have accessibility features that can’t be recreated in a traditional library setting. With text-to-speech options and text enlargement features, students with learning disabilities or visual impairments can have more autonomy in consuming information.
In addition, students with learning disabilities can learn at their own pace. Where traditional libraries may limit the amount of time a student can have a book checked out, digital libraries don’t. Students can have free access to the same e-book or resources for months as opposed to just a few weeks.
3. Simultaneous Access
Unless there are multiple copies of the same title, only one person can have a book checked out at a time. This is one of the biggest restrictions of physical libraries. Digital libraries eliminate this problem.
Using a digital environment, multiple people can read the same books or articles at the same time. This feature can significantly reduce the wait time to read popular resources, simplifying the research process.
4. Searchability Ease
E-resources simplify searchability. Students can search for topics or terms within the text and get results in seconds instead of sitting there flipping through pages of a physical copy for hours.
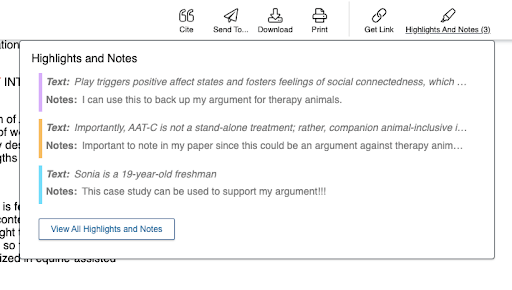
Plus, e-books and other resources have options to add bookmarks, highlight text, and leave notes throughout the copy, making navigation back to those specific sections easy.
Gale’s Academic OneFile does this in an efficient way. Their toolbar of services has one strictly for “highlights and notes.” When you want to refer back to a previous note, you can do so with ease by clicking on the specific note under the “highlights and notes” button.
5. Up-To-Date Information
Textbooks, encyclopedias, and other reference materials with multiple editions are constantly being updated with new information. To purchase these new editions, physical libraries must wait for them to be printed, and they must have adequate funding to do so.
In a digital environment, these resources can be edited and read by students faster than ever because there are no wait times for printing and delivery. If the school already has a digital library subscription like EBSCO e-books, getting updated copies can be done at an inexpensive and faster rate.
6. Interactive Features
Not sure what a vocabulary word means? Or maybe you want to explore a topic more? The interactive features of e-books like hyperlinks to the book’s glossary or a trusted outside source can quickly help redirect readers to the information they’re looking for in a way that paper books can’t.
Some digital library subscriptions have increased interactive abilities to support different age groups. For instance, POWER Library has a folder titled “POWER Kids” with resources designed for middle school students and below.
The elementary school resource called “BookFlix” gives younger students the opportunity to explore and learn on their own. They can watch a story being read or listen to an audio recording that reads the book to them as they flip through the virtual pages. They can also participate in activities to practice reading comprehension.

Advantages of Digital Libraries: Educational Implications
We’ve covered the advantages that digital libraries present to students, but what does that mean for education as a whole? For starters, they give students early exposure to technology. Our world is becoming more digital each day, so getting them familiar with technology from an early age will help set them up for success as they grow.
The biggest implication that digital libraries can have on the education system, however, is creating equity. Digital libraries can support lower-income schools by providing them with updated textbooks and materials that other high-income schools can purchase with no problem.
This can help narrow — and over time, close— the gap between schools in low and high-income areas. Less money will be spent buying thousands of physical textbooks and instead, can be reserved for a digital library subscription where only one copy needs to be purchased.
As these districts start to gain access to better resources using their digital library subscriptions, they can then help underserved students overcome disadvantages and set them up for success later in life.
How to Access a Digital Library
There are tons of digital libraries available to schools and universities, but did you know that you can join a digital library if you’re no longer a student? Most public libraries have some version of a digital library that you can access with your library card.
POWER Library is a government-funded electronic library that is accessible to all Pennsylvania residents. All you need to do to access thousands of titles is register for an eCard.
By now, it’s clear the debate of digital vs. physical libraries is so much deeper than having a preference for a paper copy. After breaking down the question of what is a digital library and exploring its advantages, it’s easy to see the impact that digital libraries have on education.
